|
Cu IDHA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
INTRODUCTION OF IDHA CHELATES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The chelating agents are used in a variety of applications including: ★Detergents; ★Agricultural nutrients; ★Industrial cleaners; ★Paper industry; ★Photography. In agriculture chelated micronutrients prevent, correct and minimize defficiencies, thus increase yields and efficiency of nutrition. Traditionally, chelating agents are poorly biodegradable, accumulate in the environment and have been detected in surface waters of rivers, lakes, and in soils. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MANUFACTURER INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
To comply with the rules of green chemistry, PPC Adob in cooperation with LANXESS GmbH has developed the production process of readily biodegradable chelates (IDHA-brand), which are subject to a joint patent application. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IDHA chelates are applied in agriculture as: ★Foliar sprays; ★Soil application; and in horticulture in: ★Hydroponics; ★Fertigation. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
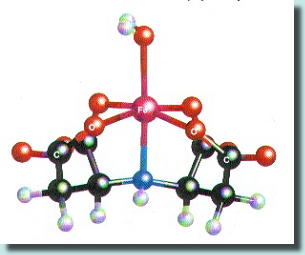
From chemical point of view D,L Aspartic acid N-(1,2-dicarboxyethyl) tetrasodium salt is a pentadentate ligand, which forms octahedral structure with metal ions as presented on the figure below The reaction between the anion IDHAm- and a metal cation Men+ is a reversible one and forms a 1:1 complex. IDHAm-+ Men+ = IDHA Me(m-n)- KIDHAMe= [IDHAMe(m-n)-] / [IDHAm][Men-] The pK values show that IDHA complexes are of moderate strength, however, enable to apply micronutirents in an available form for the plants.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
In solid form
In liquid form
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
OTHER PRODUCTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PPC ADOB offers also: ★Multicomponent micronutrients based on IDHA chelates; ★Chelated micronutrients in other fertilizers (magnesium nitrate, calcium nitrate, Calmag). All the above mentioned products are available in both solid and in liquid form. The content of the chelated micronutrients and their concentration can be adjusted to the needs of specific crops. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BIODEGRADATION OF CHELATES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
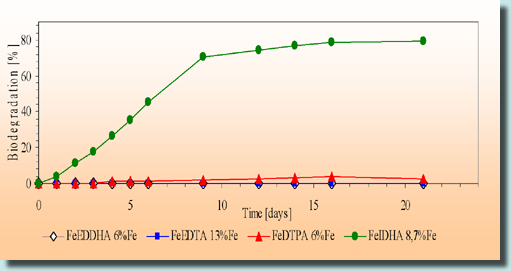
Characteristics of EDTA and other commercial chelates: ★resistant to decomposition by bacteria, not biodegradable; ★not environment friendly. The biodegradation tests of FeIDHA: ★carried out according to OECD directive 301E, and OECD 302B. The directives set minimal decomposition levels for readily biodegradable chemicals within 28 days; ★comparison with different commercial iron chelates (EDTA, DTPA, EDDHA). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The biodegradation tests of FeIDHA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The degree of biodegradation is calculated by expressing the concentration of DOC (dissolved organic carbon) removed to the percentage of initially present concentration. Adob’s IDHA chelates can be regarded as readily biodegradable as they decompose acc. To OECD 301C in 78% after 28 days, and acc. To OECD 302E in 89% in 28 days. They may even be described as rapidly biodegradable. The results have shown that Adob’s IDHA chelate has by far the best biodegradation in comparison with other commercial chelates.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stability at different pH |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
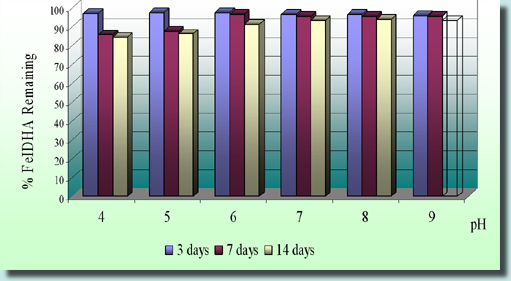
IDHA chelates were also checked for their stability at different pH. The amount of Fe IDHA remaining in solution at different pH was studied. The pH of 10-5 M Fe IDHA with 5 ml M Ca Cl2 solution was adjusted with HCl or NaOH. Samples were placed in a shaker bath for 3,7, or 14 days. After the agitation, chelated Fe was measured by ion pair Chromatography. The results have shown, that for most pH ranges the Fe remains in solutions after those three periods. Therefore, Adob’s IDHA can be regarded as stable.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TESTS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In order to check IDHA efficiency, the chelates have been tested at the
following institutions:
★Universidad Autonoma de Madrid – Spain ★Landwirtschaftlische Untersuchungs um Forschungsamt Hannover – Germany ★Akademia Rolnicza Poznan – Poland ★Hebrew University Jerusalem – Israel ★Katholieke Universiteit Leuven – Belgium IDHA efficiency was tested in comparison with other commercial chelates. Among others the following tests were carried out: ★Soybean in hydroponic ★Chinese cabbage in soil ★Cucumber in hydroponic The results of selected tests are presented below. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TEST - HYDROPONICS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The test of FeIDHA on soybean in hydroponics in comparison with other
commercial Fe chelates
Soybean is one of the best studied susceptible crop, with low Fe chelate reductase activity. This experiment has been done in a growth chamber. ★ pH was buffered at 7,5 with 0,1 mM Hepes. ★Water was added every two days and the solution was renewed every week ★5 mM Fe was added at the treatments in four replications The result have proved that Fe IDHAapplication was better than FeEDTA effecting thus in higher yield. Results soybean test
Soybean in hydroponics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TEST - SOIL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
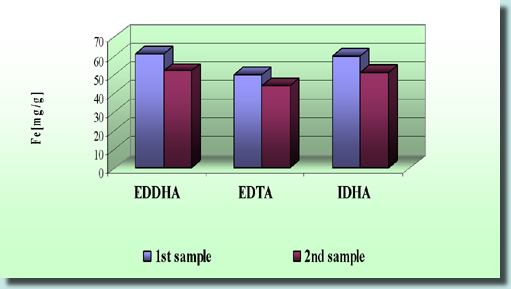
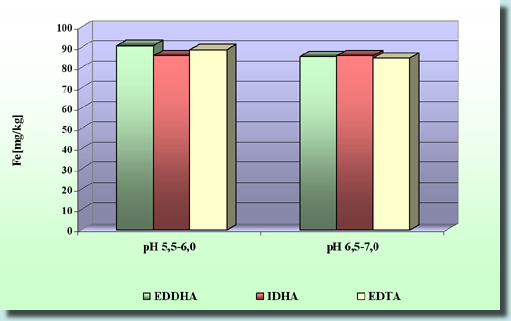
| The test of FeIDHA on Chinese cabbage in soil in comparison with other
commercial Fe chelates Plants were used in a biological experiment. ★Plants were seed and germinated on peat-clay soil in two different pH ranges (5.5-6.0 and 6.5-7.0). ★30 mg of Fe/l of water was added. After 26 days head of Chinese cabbage were washed, weighted and dried. In the case of the FeIDHA the Fe content in dry leaves is similar to those in which EDDHA and EDTA were used. Results Chinese cabbage
Chinese cabbage in soil
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CONCLUSIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ★IDHA chelates are an enviroment friendly alternative to conventional complexing
agents.
★In June 2001 Bayer was awarded the US President Green Chemistry Challange Award for its product. ★This agent is characterized by excelletnt chelation capabilities, especially for iron-III, manganese-II, zinc-II and coppper-II ★The new micronutrients may even be called rapidly biodegradable, which is very important especially because of strong criticism of EDTA, and its limited application as chelation agent in many industries. |